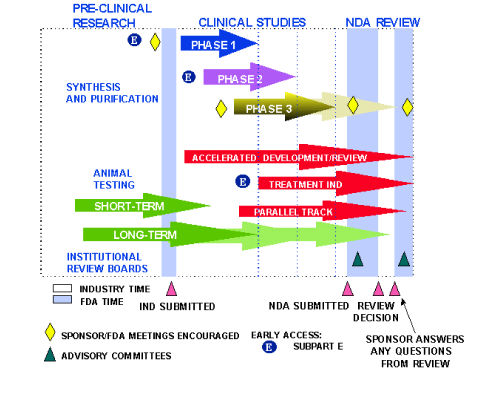
Pharmaceutical Development
DOSAGE FORMS & ROUTE OF ADMINISTRATION
Dosage forms (also called unit doses) are pharmaceutical drug products presented in a specific form for use. They contain a mixture of active ingredients and inactive components (excipients), configured in a particular way and apportioned into a specific dose.
Dosage forms vary depending on the method and route of administration, which can include many types of liquid, solid, and semisolid forms. Common dosage forms include tablets, capsules, syrups, creams, and injectables.
A combination drug (or fixed-dose combination; FDC) is a product that contains more than one active ingredient.
The route of administration (ROA) for drug delivery depends on the dosage form of the substance. Different dosage forms may be available for a particular drug, especially if certain conditions restrict the ROA. A specific dosage form may also be required due to issues such as chemical stability or pharmacokinetic properties.
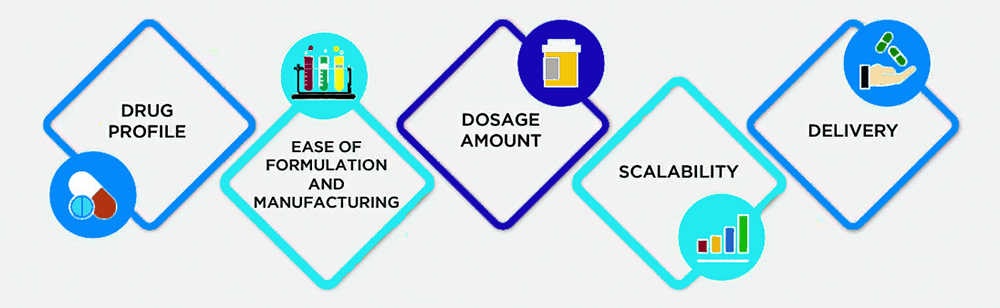
CHOOSING A DOSAGE FORM
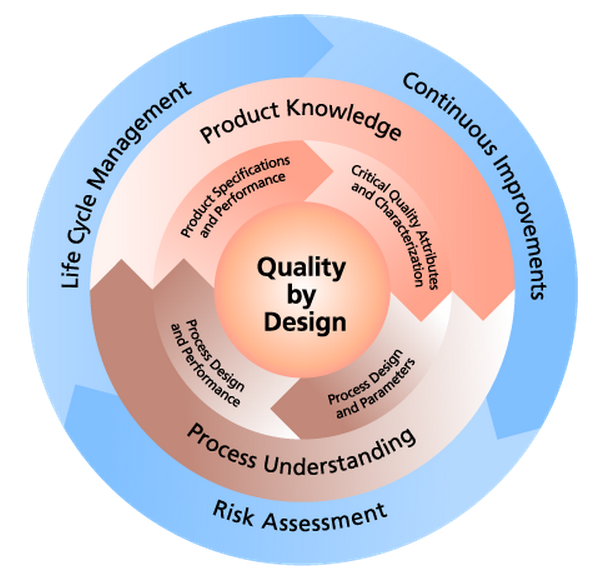
CHEMISTRY MANUFACTURING & CONTROLS
Chemistry Manufacturing & Controls (CMC) is an essential part of the Drug Development Process. CMC is a term used when drug developers define their investigative drug substance, establish manufacturing methods for that drug, and develop a strategy for controlling the quality and stability of the product from early phases through post-approval production.