
Document Management
Document management involves the systematic organization, storage, retrieval, and protection of documents throughout their lifecycle. It includes digitalizing paper-based records, implementing version control, maintaining data security, and ensuring compliance with industry regulations.
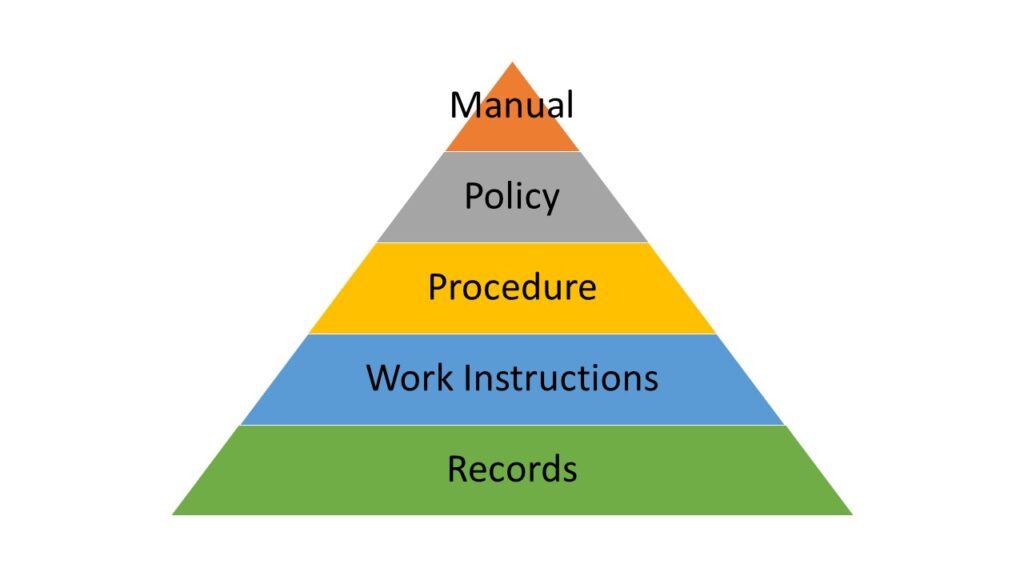
Good Documentation Practices
Good Documentation Practice (GDP) is a systematic procedure of preparing, reviewing, approving, issuing, recording, storing and archiving of documents.
KEY PRINCIPALS OF GDP:
- Attributable: Documentation should clearly identify who recorded the data/information, including their name, date, and time (as appropriate).
- Legible: Documents must be easy to read and understand, ensuring clarity and avoiding ambiguity.
- Contemporaneous: Information should be recorded at the time it occurs, or as soon as possible afterwards.
- Original: Maintain original records whenever possible, and ensure any copies are accurate and traceable to the original.
- Accurate: Data should be free from errors and omissions, ensuring the integrity of the information.
- Complete: All relevant information should be included in the documentation, providing a comprehensive record.
- Traceability: Ensure documents can be traced back to their source and purpose, including the study, study phase, and personnel involved.
- Clear and Concise: Information should be presented in a clear and concise manner, avoiding unnecessary jargon or complexity.
- Approved and Signed: Documents should be approved, signed, and dated by the appropriate and authorized personnel.
- Unambiguous Contents: The title, nature, and purpose of each document should be clearly stated.
- Orderly Layout: Documents should be organized in a logical and easy-to-check manner.
- Reproduced Documents: Reproduced documents should be clear and legible, ensuring accuracy and readability.
- Data Integrity: Maintain the integrity of data throughout the documentation lifecycle, including storage, retrieval, and analysis.
- Electronic Records: When using electronic records, ensure they meet the requirements of 21 CFR Part 11, which regulates electronic signatures and electronic records.
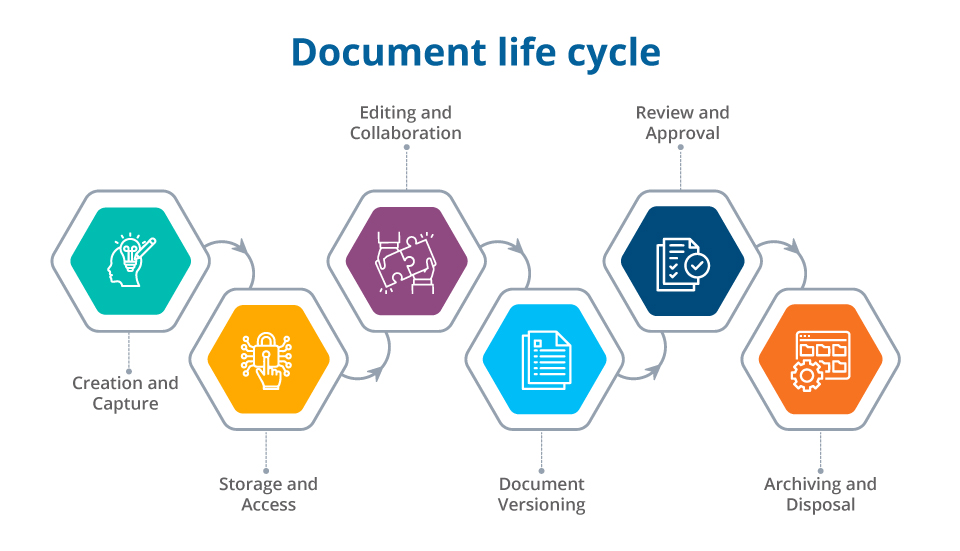
DOCUMENT MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE
Document Management Software is a computerized system used to store, share, track, and manage documents, often including features like version control, automated workflows, and secure access. Document management software is essentially software that helps organizations manage their digital documents and related information.
- Storage: Document management software provides a central repository for storing documents in a digital format.
- Organization: It allows users to organize documents using various methods, such as folders, tags, and metadata.
- Sharing and Collaboration: Document management software enables users to easily share documents with others and collaborate on them.
- Version Control: It tracks different versions of a document, allowing users to revert to previous versions if needed.
- Workflow Automation: Document management software can automate tasks related to document management, such as routing documents for approval or sending notifications.
- Security: It provides access control and security features to protect sensitive documents.
- Search: Document management software often includes powerful search capabilities to quickly find specific documents or information.
